
 |
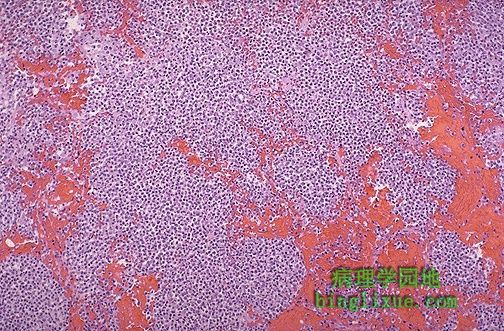
毒力较强细菌性肺炎或更严重的肺炎可能与肺组织破坏和出血有关。图中不见肺泡壁,因为早期有脓肿形成。还存在出血。 More virulent bacteria and/or more severe pneumonias can be associated with destruction of lung tissue and hemorrhage. Here, alveolar walls are no longer visible because there is early abscess formation. There is also hemorrhage. |
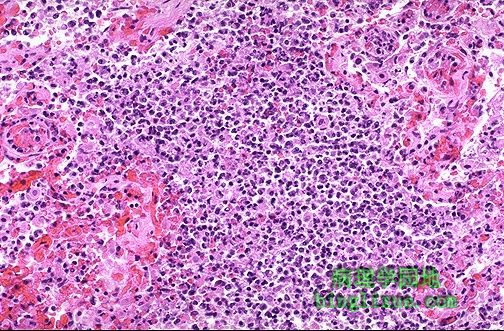 |
高倍镜下,可看到早期的脓肿肺炎。肺泡壁不很清楚,仅有嗜中性粒细胞。 At higher magnification, early abscessing pneumonia is shown. Alveolar walls are not clearly seen, only sheets of neutrophils. |
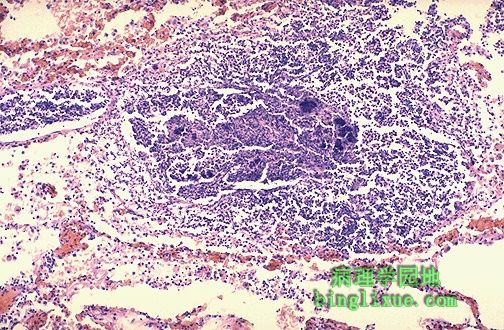 |
就如同深蓝色细菌菌落暗示存在肺吸入性或血液播散性炎症一样,更局限化的脓肿灶包含嗜中性细胞。经口-咽吸入物质包括细菌。血液播散性肺炎可由败血症或感染性心内膜炎引起。 This more focal abscess containing a neutrophilic exudate as well as dark blue bacterial colonies suggests aspiration or hematogenous spread of infection to the lung. Aspirated material from the oral-pharyngeal region contains bacterial flora. Hematogenous spread of infection to lungs could occur from septicemia or from infective endocarditis involving the right side of the heart. |
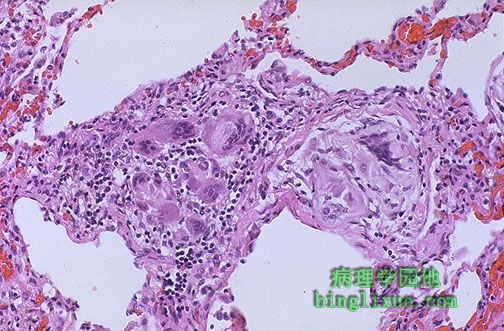 |
高倍镜下,可见对吸入物产生的异物巨细胞反应。吸入物如同胃内容物一样由于化学刺激物的作用可引起炎症。 There is a localized foreign body giant cell response to the aspirated material seen here at high magnification. Aspirated material may also produce inflammation from chemical irritation, as with gastric contents. |
 |
几乎整个右肺中叶都存在慢性脓肿。脓肿区域是黄褐色,非常坚韧。此处引起感染的因素是诺卡菌属,主要引起慢性脓肿。 Almost the entire middle lobe of this right lung is involved by a chronic abscess as seen here on section. The area of abscess is yellow tan, and it was very firm.The infectious agent responsible here was Nocardia, which is known to produce chronic abscessing inflammation. |
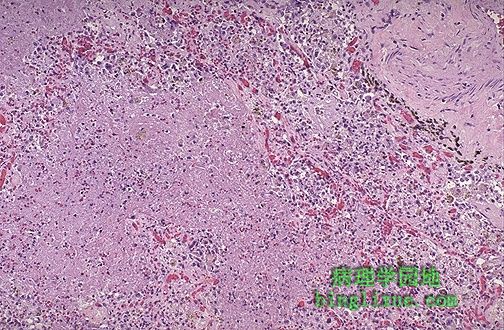 |
慢性脓肿,左边有大面积的粉红色坏死组织,坏死组织被肉芽组织包绕,肉芽组织内毛细血管丰富,供血充足。 This is a microscopic appearance of chronic abscessing inflammation with large areas of pink necrotic tissue present on the left that are bordered by granulation tissue with numerous prominent capillaries filled with blood. |
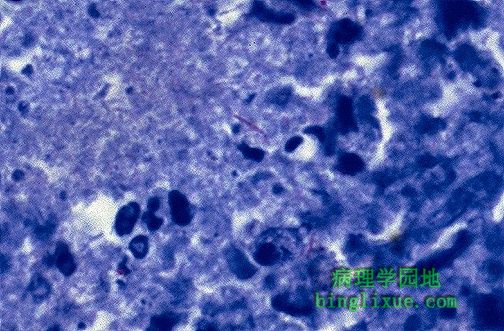 |
中央可见抗酸染色显示的一长丝状微生物,暗红色。这是诺卡菌属的特征。 An acid fast stain demonstrates a long filamentous organism in the center that is dark red. This is typical for Nocardia. |
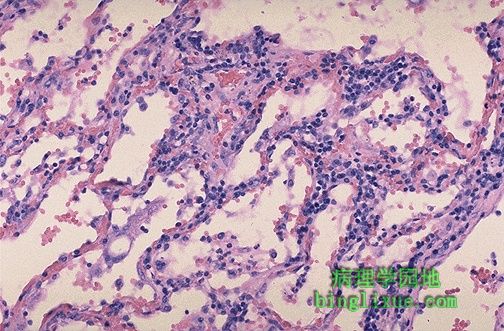 |
病毒性肺炎间质淋巴细胞浸润。没有肺泡腔渗出物。因此,很少咳嗽。病毒性肺炎最常见的病原是流感病毒,副流感病毒,腺病毒,以及呼吸道合胞体病毒( RSV 主要发生于儿童)。巨细胞病毒则发生在免疫缺乏病人。 Here is the microscopic appearance of a viral pneumonia with interstitial lymphocytic infiltrates. Note that there is no alveolar exudate. Thus, the patient with this type of pneumonia will probably not have a productive cough. The most common causes for viral pneumonia are influenza, parainfluenza, adenovirus, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV appears mostly in children). Cytomegalovirus can appear in immunocompromised hosts. |
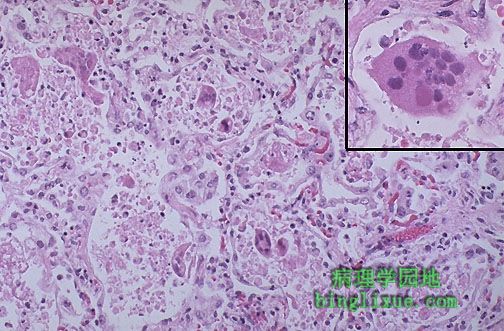 |
儿童呼吸道合胞体病毒( RSV )。注意巨细胞,它是细胞病理效应的一部分。插图显示典型的巨细胞,圆形,有粉红色胞质包涵体。RSV是2岁以下儿童患肺炎的主要原因,同时也是1~6 个月或稍大的婴幼儿死亡的一个原因。 This is respiratory syntytial virus (RSV) in a child. Note the giant cells which are part of the viral cytopathic effect. The inset demonstrates a typical giant cell with a round, pink intracytoplasmic inclusion. RSV accounts for many cases of pneumonia in children under 2 years, and can be a cause for death in infants 1 to 6 months of age or older. |
 |
类脂性肺炎,左边有一边界模糊的浅黄*色区域。黄*色外观解释了“金色”肺炎这个术语。类脂性肺炎主要有两种类型:内源性和外源性。 Here is the gross appearance of a lipid pneumonia in which there is an ill-defined, pale yellow area on the left. This yellow appearance explains the term "golden" pneumonia. There are two main types of lipid pneumonia: endogenous and exogenous. |