
 |
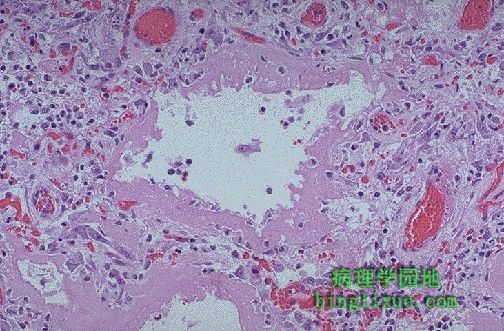
弥漫性肺泡损伤(DAD)的肺,DAD是许多严重肺损伤的最后结局。DAD的早期,有透明膜隔开肺泡,如图所见。 This is the microscopic appearance of diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) in the lung. DAD is simply the final common pathway for a variety of severe lung injuries. In early DAD, there are hyaline membranes, as seen here, lining alveoli. Later, type II pneumonocyte proliferation and then interstitial inflammation and fibrosis are seen. High oxygen tensions needed to treat the hypoxia resulting from DAD and its etiologies further potentiates this disease. |
 |
此处不考虑限制性肺病的病原学,许多最终发生了广泛的纤维化。如图正在机化的弥漫性肺泡损伤病人,外观是典型的蜂窝肺,因在不规则致密纤维结缔组织间有较多含气孔而得名。 Regardless of the etiology for restrictive lung diseases, many eventually lead to extensive fibrosis. The gross appearance, as seen here in a patient with organizing diffuse alveolar damage, is known as "honeycomb" lung because of the appearance of the irregular air spaces between bands of dense fibrous connective tissue. |
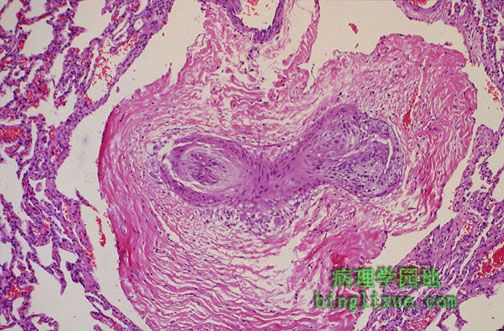 |
限制性和阻塞性肺病都能影响肺循环。 Both restrictive and obstructive lung diseases can affect the pulmonary arterial circulation. The loss of normal lung parenchyma leads to pulmonary hypertension that leads to thickening of the small arteries along with reduplication to form a plexiform lesion, as seen here in a peripheral pulmonary artery. |
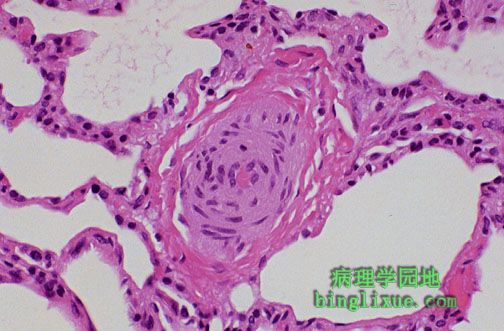 |
图示肺动脉高压见明显增厚的肺外周小动脉。较大的肺动脉显示伴有肺动脉高压的动脉粥样硬化。 Seen with pulmonary hypertension are small peripheral pulmonary arteries that are quite thickened. The larger pulmonary arteries demonstrate atherosclerosis with pulmonary hypertension. |
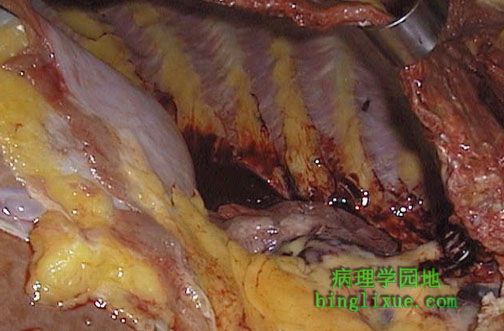 |
图示肺不张,见右肺萎陷。图示血液充满胸膜腔(血胸),导致肺不张。但是肺不张也可由胸腔内充满气体(气胸)、漏出液(胸水)、淋巴(乳糜胸),或者脓性渗出物(脓胸)引起。 The right lung is collapsed. This is atelectasis. In this case, blood filled the pleural cavity (hemothorax), but atelectasis could also result from filling the chest with air (pneumothorax), transudate (hydrothorax), lymph (chylothorax), or purulent exudate (empyema). |
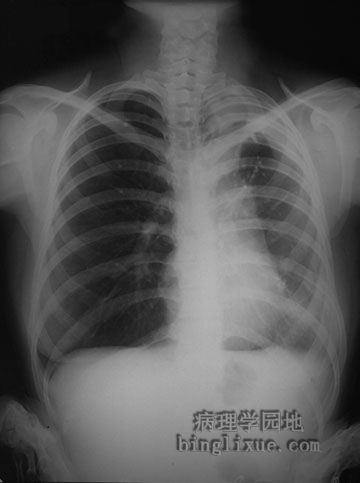 |
X线显示右侧气胸,可见心影左移。气胸发生于穿透性的胸部损伤、肺气肿肺大疱破裂、正压通气。空气进入胸膜腔挤压肺组织。图为张力性气胸,因呼吸时活瓣样的结构使气体漏入到胸膜腔的越来越多,纵膈移位。闭式引流管可排出胸膜腔内的气体使萎缩肺膨胀。 This radiograph demonstrates a right pneumothorax. Note the displacement of the heart to the left. A pneumothorax occurs with a penetrating chest injury, inflammation with rupture of a bronchus to the pleura, rupture of an emphysematous bulla, or positive pressure ventilation. The escape of air into the pleural space collapses the lung. The example seen here is a "tension" pneumothorax shifting the mediastinum, because a "ball-valve" air leak is increasing the air in the right chest cavity. A chest tube can be placed to re-expand the lung. |
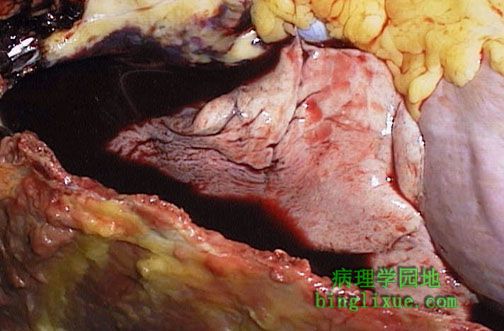 |
图示血胸。外伤后,大量出血,充满胸膜腔,使右肺萎陷,并在血性液体中飘浮。 The right lung is atelectatic and floating in bloody fluid filling the right chest cavity as a consequence of trauma. This is a hemothorax. |
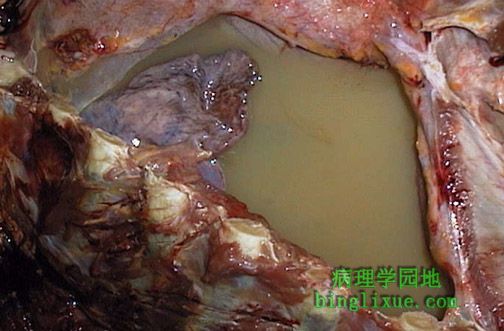 |
图示乳糜胸,右胸膜腔充满黄褐色云絮状液体。该淋巴瘤病人病变累及胸部和腹部淋巴管引起乳糜液聚集。右肺明显萎陷。 The right pleural cavity is filled with a cloudy yellowish-tan fluid, characteristic for a chylothorax. In this case, lymphoma involving the lymphatics of the chest and abdomen led to the collection of chylous fluid. The right lung is markedly atelectatic. |
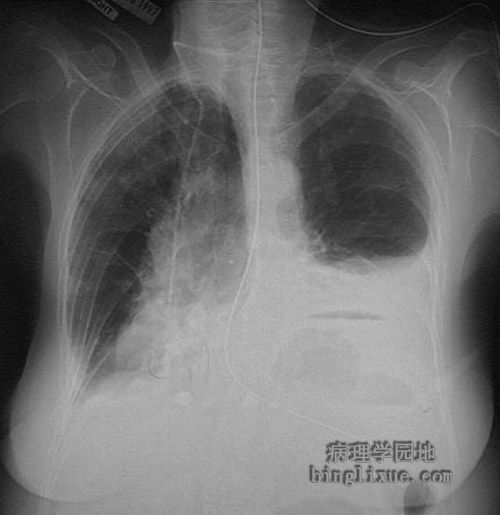 |
X线显示左胸膜腔积液。积液可能是浆液、血性液、血性浆液,也有可能是乳糜液(少见),如果脓液渗出将引起脓胸。可见膈下的胃内气液平面。 This radiograph demonstrates fluid in the left pleural cavity. This pleural effusion could result from a transudate (serous effusion) or from hemorrhage (hemothorax), or serous fluid tinged with blood (serosanguinous effusion). This effusion could be chylous (which is quite rare). A purulent exudate at this location may be termed empyema. An air-fluid level is seen in the stomach below the dome of the left diaphragmatic leaf. |