
 |
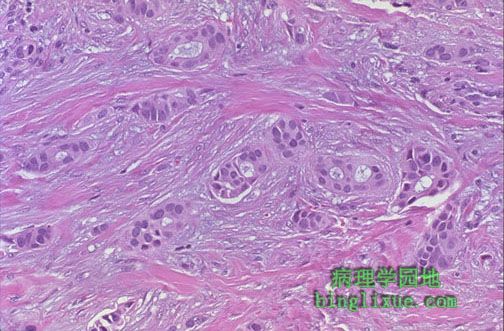
高倍见中央区导管内癌细胞的多形性(筛型),还可见瘤细胞浸润至间质与脂肪而形成浸润性导管癌。 At high magnification, the pleomorphism of the carcinoma cells within the duct in the center (in a cribriform pattern), as well as the neoplastic cells infiltrating through the stroma and fat, can be seen with this infiltrating ductal carcinoma. |
 |
高倍镜下见乳腺浸润性导管癌分化较差,癌细胞异型性大。确定这些细胞雌激素与孕激素受体阳性与否对治疗与预后也很重要。 At high magnification, this infiltrating ductal carcinoma of breast is poorly differentiated, with very pleomorphic cells. It would also be important for treatment and prognosis to determine if these cells were estrogen and progesterone receptor positive. |
 |
乳腺癌的多样性如所谓的胶样癌或黏液癌。如图可见丰富的淡蓝色黏液。癌细胞好象漂浮在黏液里,这种类型多见于较大年龄的妇女且生长较慢;要是它的组织学形态良好,预后将好于非黏液性浸润性癌。 This variant of breast cancer is known as colloid, or mucinous, carcinoma. Note the abundant bluish mucin. The carcinoma cells appear to be floating in the mucin. This variant tends to occur in older women and is slower growing, and if it is the predominant histologic pattern present, then the prognosis is better than for non-mucinous, invasive carcinomas. |
 |
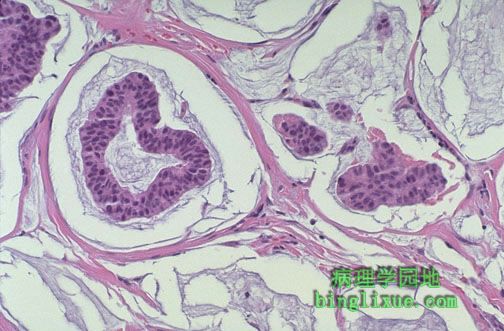
图示小叶原位癌。小叶原位癌由末端乳腺导管与腺泡内的瘤性细胞增生形成。细胞小而圆。尽管这些病变处于低分级,在同侧或对侧乳腺有30%发展成浸润性癌的风险。 Lobular carcinoma in situ is seen here. Lobular CIS consists of a neoplastic proliferation of cells in the terminal breast ducts and acini. The cells are small and round. Though these lesions are low grade, there is a 30% risk for development of invasive carcinoma in the same or the opposite breast. |
 |
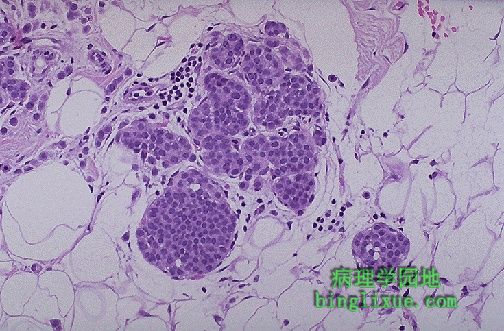
图示浸润性小叶癌。肿瘤见于乳腺末端小管。大约5%到10%的乳腺癌是这种类型。对侧乳腺有20%的患癌风险,且其大多数在同一乳腺呈多中心发生。 Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast is shown here. This neoplasm arises in the terminal ductules of the breast. About 5 to 10% of breast cancers are of this type. There is about a 20% chance that the opposite breast will also be involved, and many of them arise multicentrically in the same breast. |
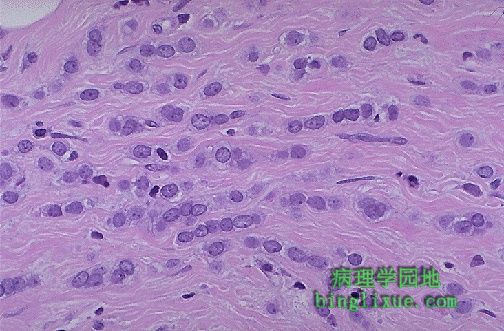 |
高倍在纤维间质中可见浸润性小叶癌癌细胞单行排列的特征性病变。多形性不大。 At high magnification, the characteristic "Indian file" strands of infiltrating lobular carcinoma cells are seen in the fibrous stroma. Pleomorphism is not great. |
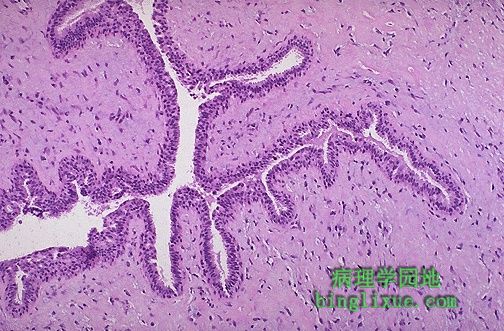 |
图示乳腺分叶状肿瘤。它们源于小叶间质,但不象纤维腺瘤,它们不常见而且大的多。它们分级低因此很少转移。它们比纤维腺瘤细胞更丰富。 A phyllodes tumor of the breast is shown here. They arise from interlobular stroma, but unlike fibroadenomas are not common and are much larger. They are low-grade neoplasms that rarely metastasize. They are more cellular than fibroadenomas. Projections of stroma into the ducts create the leaf-like pattern for which these tumors are named (from the Greek word phyllodes meaning leaf-like). |
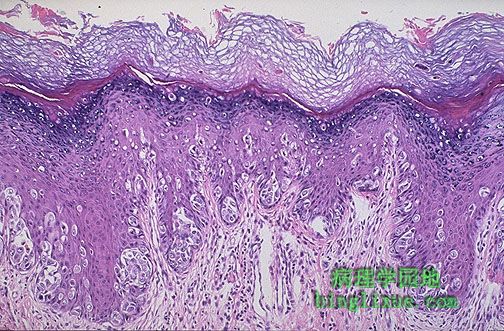 |
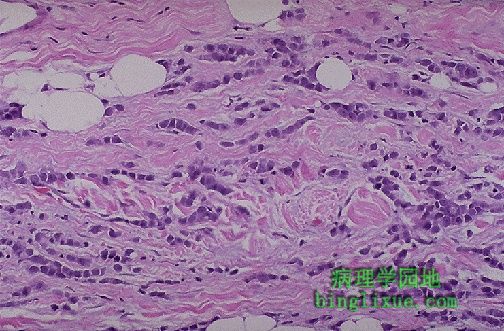
这里显示了乳腺Paget病。值得注意的是皮肤过度角化,使其产生粗糙的红色起鳞屑外形,且常有溃疡。浸润至真皮的大细胞说明位于下方的导管原位癌或浸润性导管癌向上皮内侵犯。 Paget's disease of the breast is shown here. Note the overlying hyperkeratosis of the skin, which helps to produce the rough, red, scaling appearance seen grossly, and there is often ulceration. The large cells infiltrating into the epidermis represent intraepithelial extension of an underlying ductal carcinoma in situ or invasive ductal carcinoma. |
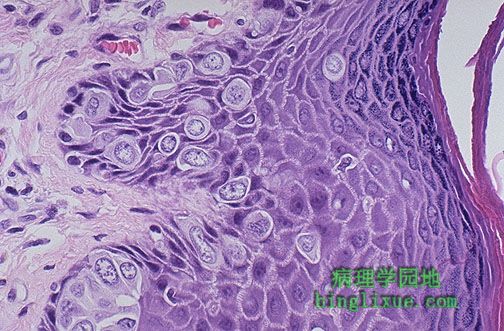 |
高倍放大后,可见乳腺Paget病大的Paget氏细胞有着丰富清晰的细胞质而且或单个或成簇地见于表皮。Paget氏细胞的细胞核有异型性而且常有显而易见的核仁(尽管这里未见到)。 At high magnification, the large Paget's cells of Paget's disease of breast have abundant clear cytoplasm and appear in the epidermis either singly or in clusters. The nuclei of the Paget's cells are atypical and, though not seen here, often have prominent nucleoli. |
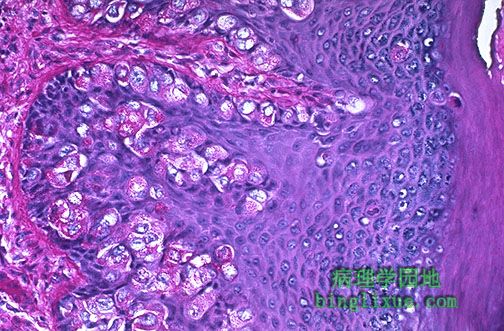 |
过碘酸希夫染色显示了乳腺Paget病Paget氏细胞里的黏蛋白。此为他们起源于下方的导管癌的证据。通过免疫过氧化物酶染色可知他们也是角蛋白阳性与上皮膜抗原阳性。 A PAS stain demonstrates mucin within the Paget's cells of Paget's disease of the breast. This is evidence for their origin from an underlying ductal carcinoma. By immunoperoxidase staining, they will also be keratin positive and epithelial membrane antigen positive. |