
 |
At high magnification, the normal colonic epithelium at the left contrasts with the atypical epithelium of the adenomatous polyp at the right. Nuclei are darker and more irregularly sized and closer together in the adenomatous polyp than in the normal mucosa. However, the overall difference between them is not great, so this benign neoplasm mimics the normal tissue quite well and this, therefore, well-differentiated. 高倍镜:左侧为正常的结肠粘膜上皮,与之相比右侧为腺瘤性息肉的非典型增生上皮。腺瘤性息肉与正常粘膜上皮细胞相比细胞核染色加深、大小不一。然而它们之间的不同不是很大,因此这种良性肿瘤与正常的组织相似性较大,分化较好。 |
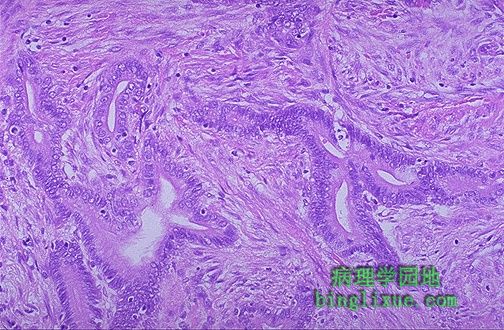 |
The infiltrating glands of this colonic adenocarcinoma demonstrate less differentiation than the adenomatous polyp, although they still resemble glands. In general, less differentiation means a greater likelihood of malignant behavior. 结肠腺癌浸润的腺体与腺瘤性息肉虽然都可以看出类似于腺体,但前者分化程度更低。 一般来说,分化程度差的肿瘤恶性程度更高。 |
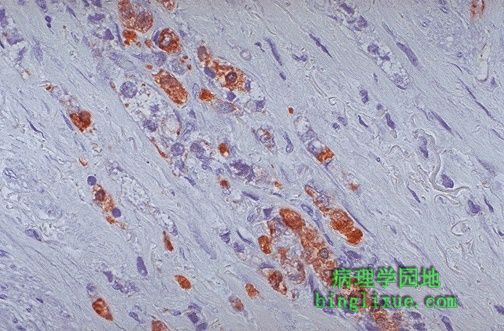 |
This gastric adenocarcinoma is positive for cytokeratin by immunoperoxidase(免疫过氧化物酶). This is a typical staining reaction for carcinomas and helps to distinguish carcinomas from sarcomas and lymphomas. Immunoperoxidase staining is helpful to determine the cell type of a neoplasm when the degree of differentiation, or morphology alone, does not allow an exact classification. 胃腺癌对免疫过氧化物酶染色反应呈角蛋白阳性,这是癌的典型染色反应,用于癌与肉瘤、淋巴瘤的鉴别。 当依赖分化程度或单纯从形态学角度不能进行精确分类时,免疫过氧化物酶染色有助于判断肿瘤细胞的类型。 |
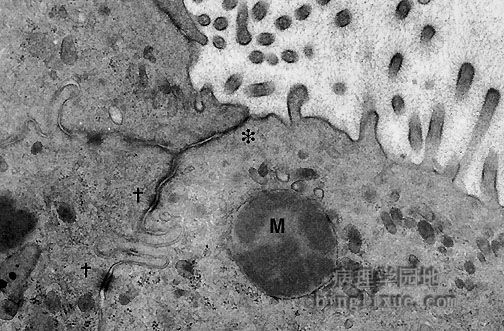 |
By electron microscopy, features of a carcinoma can be seen. This adenocarcinoma demonstrates several features typical of a neoplasm of epithelial origin, including the junctional complex (tight junction at the asterisk and the desmosomes at crosses). The mucin granule (M) and lumenal microvilli at the upper right are also typical for an adenocarcinoma. 通过电镜,可以清晰看出癌的几个特征。图示上皮源性腺癌的几个特征,包括连接复合体(星号处表示:紧密连接,“十”字处显示:细胞间桥),粘蛋白颗粒(标M的地方)和右上方中空的微绒毛也是腺癌的典型的特征。 |
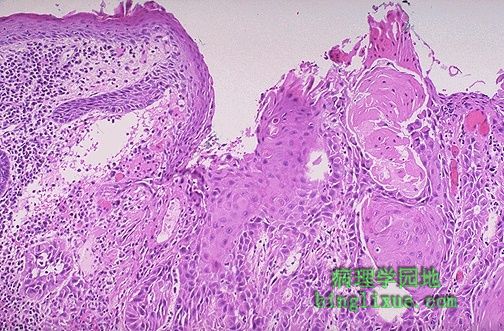 |
The normal squamous epithelium at the left merges into the squamous cell carcinoma at the right, which is infiltrating downward. The neoplastic squamous cells are still similar to the normal squamous cells, but are less orderly. This is a well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma. 左侧为正常鳞状上皮,右侧为鳞状细胞癌(向深部组织浸润)。肿瘤的鳞状细胞与正常的鳞状细胞结构相似,但排列紊乱。 图示:高分化鳞状细胞癌 |
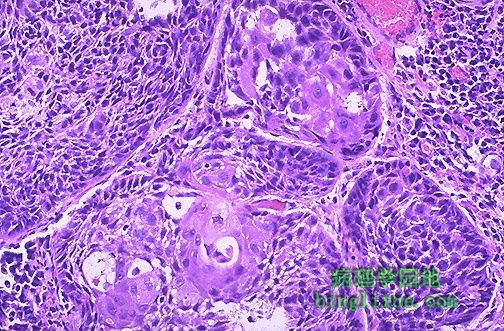 |
Here is a moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma in which some, but not all, of the neoplastic cells in nests have pink keratin. In general, neoplasms with less differentiation are more aggressive. 图示:中度分化的鳞状细胞癌。 不是所有的肿瘤细胞形成的癌巢中央都有角蛋白(角化珠)。一般来说,分化程度越肿瘤越富有侵袭性。 |
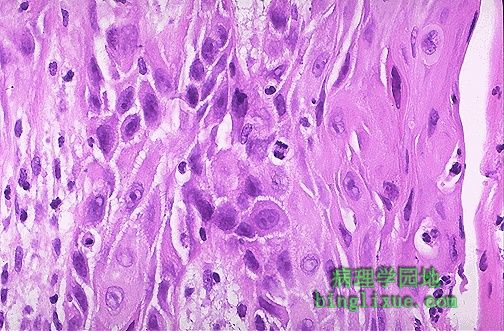 |
At high magnification, this squamous cell carcinoma demonstrates enough differentiation to tell that the cells are of squamous origin. The cells are pink and polygonal in shape with intercellular bridges (seen as desmosomes or "tight junctions" by electron microscopy). However, the neoplastic cells show pleomorphism, with hyperchromatic nuclei. A mitotic figure is present near the center. 高倍镜示:鳞状细胞癌分化程度较高,从此足以判断来源于鳞状上皮。细胞呈粉红色、多边形,并可见细胞间桥(通过电镜看到的桥粒或紧密连接)。肿瘤细胞的多形性明显,细胞核深染。中央区域可见核分裂象。 |
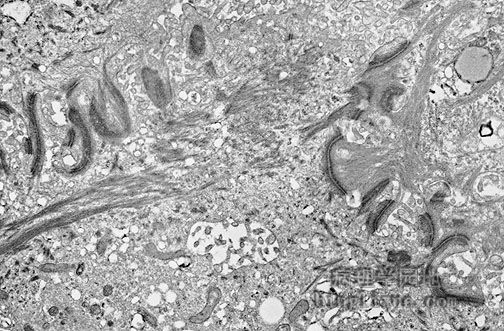 |
Features of a carcinoma are seen in this electron micrograph. This squamous cell carcinoma demonstrates many desmosomes, along with cytoplasmic tonofilaments streaming to the left. 电镜示:鳞状细胞癌 许多桥粒清晰可见,沿着细胞浆张力丝向左延伸。 |
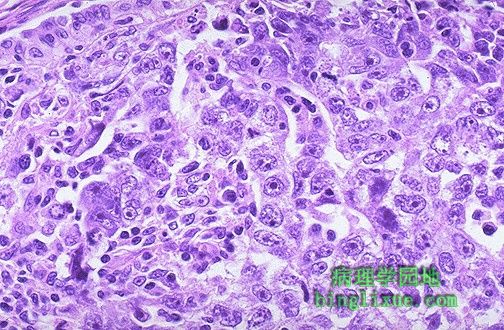 |
This neoplasm is so poorly differentiated that it is difficult to tell what the cell of origin is. It is probably a carcinoma because of the polygonal nature of the cells. Note that nucleoli are numerous and large in this neoplasm. Neoplasms with no differentiation are said to be anaplastic. 肿瘤分化很差,以至于很难判断组织来源。这可能是一种源于多形性细胞的一种癌。在肿瘤细胞中核多且大。未分化肿瘤被称为退化发育。 |
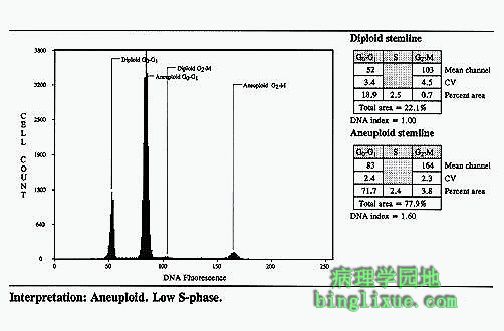 |
One measure of malignancy is aneuploidy by flow cytometry. Pictured here is the flow cytometry pattern of a breast carcinoma. The worse the neoplasm, the greater the degree of aneuploidy and the worse the prognosis. 恶性肿瘤的检测方法之一是通过流式细胞计显示异倍性。图示:乳腺癌流式细胞仪模式图。肿瘤越恶性,异倍性程度越大,报告结果就越差。 |
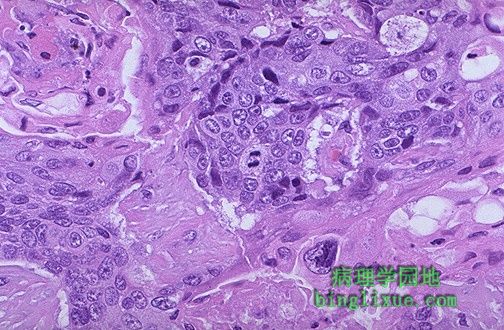 |
A mitotic figure is seen in the center, surrounded by a poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with pleomorphic cells and minimal pink keratinization. In general, mitoses are more likely to be seen in malignant neoplasms. Remember, though, that normally cells are actively dividing in bone marrow, gonads, and gastrointestinal tract. 图中央可见核分裂象,周围是低分化鳞状细胞癌的多形性癌细胞和粉红色微小的角化蛋白。 通常病理性核分裂多在恶性肿瘤中出现。 |