
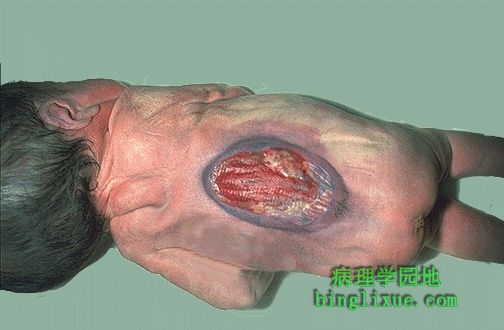
较大的胸段脊膜脊髓膨出是神经管缺陷的另一种类型。亚甲基四氢叶酸还原酶基因突变导致的遗传多态现象可增加神经管缺陷(NTD)发生的危险性。叶酸为此酶作用后的产物,同时此酶也是细胞内同型半胱胺酸的部分代谢去路。C677T和A1298C突变使母体同型半胱胺酸水平升高,增加神经管缺陷发生的危险性。母亲妊娠期前或妊娠期增加叶酸摄入,将降低神经管缺陷发生的概率。
This large mid-thoracic meningomyelocele is another form of neural tube defect (NTD). The genetic polymorphisms due to mutations in the methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase gene may increase the risk for NTDs. Folate is a cofactor for this enzyme, which is part of the pathway of homocysteine metabolism in cells. The C677T and the A1298C mutations are associated with elevated maternal homocysteine concentrations and an increased risk for NTDs in fetuses. Mothers who supplement their diets with folate prior to and during pregnancy can often reduce this risk.